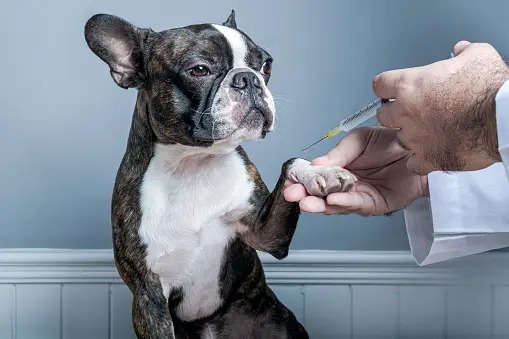
Understanding the Importance of Vaccinations for Dogs
Why Vaccinations are Important for Dogs
Vaccinations play a crucial role in safeguarding your beloved furry friend’s health. Just like humans, dogs are susceptible to various diseases that can be prevented through proper immunization. Vaccinations work by stimulating your dog’s immune system to produce antibodies, which provide protection against harmful pathogens such as viruses and bacteria. By ensuring your dog is up to date with vaccinations, you can significantly reduce the risk of them contracting serious and potentially life-threatening illnesses.
How Vaccinations Protect Your Dog’s Health
- Prevention of Common and Deadly Diseases: Vaccinations effectively guard your dog against a range of diseases that are prevalent in their environment. Diseases such as rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and hepatitis can have severe consequences for your dog’s health. Vaccinating your dog ensures they have the necessary immunity to fight off these diseases if exposed.
- Herd Immunity: Vaccinations not only protect your individual dog but also contribute to the overall health of the dog community. Achieving a substantial rate of immunization within the dog population results in the establishment of herd immunity. This phenomenon indicates that dogs lacking vaccination or possessing weaker immune systems are less likely to come into contact with disease-causing agents. This is attributed to the diminished prevalence of the disease within the community.
- Prevention of Zoonotic Diseases: Some diseases that affect dogs can also be transmitted to humans, known as zoonotic diseases. By vaccinating your dog, you not only protect their health but also minimize the risk of these diseases spreading to you and your family. Diseases like leptospirosis and canine influenza can be prevented through proper vaccination, ensuring the safety of both your dog and your household.
- Cost-effective Health Care: Investing in vaccinations for your dog is a wise financial decision. The cost of vaccinating your dog is significantly lower than the expenses associated with treating a disease or infection. By preventing diseases through vaccination, you can save yourself from the financial burden of extensive veterinary treatments and medications.
Vaccinations are vital for maintaining your dog’s health and well-being. By understanding the importance of vaccinations, you can make informed decisions about your dog’s immunization schedule, ultimately ensuring a long and happy life for your beloved pet.
Core Vaccinations for Dogs
Rabies Vaccine
The rabies vaccine is one of the most important vaccinations for dogs. It is not only crucial for the health and well-being of your furry friend but also required by law in many countries. Rabies is a deadly viral disease that affects the nervous system of animals, including dogs. It can be transmitted to humans through bites or scratches from infected animals.
By vaccinating your dog against rabies, you are not only protecting them from this fatal disease but also ensuring the safety of your family and others in the community. Puppies usually receive their first rabies shot at around 12 to 16 weeks of age, followed by regular booster shots every one to three years, depending on the local regulations.
Distemper Vaccine
The distemper vaccine is another essential vaccination that all dogs should receive. Canine distemper is a highly contagious viral illness that affects the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems of dogs. It can be spread through direct contact with an infected dog or through contact with contaminated objects such as food bowls or bedding.
Symptoms of distemper can vary but may include fever, coughing, vomiting, diarrhea, nasal discharge, and neurological signs like seizures. In severe cases, distemper can be fatal. Vaccinating your dog against distemper is crucial in preventing the spread of this disease and protecting their health. Puppies typically receive their first distemper shot at around 6 to 8 weeks of age, followed by additional booster shots until they reach adulthood.
Canine Parvovirus Vaccine
The canine parvovirus vaccine is a vital component of your dog’s vaccination schedule. Canine parvovirus is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects puppies and unvaccinated dogs. It can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected dog’s feces or contaminated environments such as parks, sidewalks, or kennels.
Parvovirus attacks the gastrointestinal system, leading to severe vomiting, diarrhea (often bloody), dehydration, and a weakened immune system. Without prompt treatment, parvovirus can result in a high mortality rate among affected dogs. Vaccination is the most effective way to protect your dog against this life-threatening disease. Puppies usually receive their first parvovirus vaccine at around 6 to 8 weeks of age, with additional booster shots until they reach adulthood.
Ensuring that your dog receives these core vaccinations is essential for their overall health and well-being. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best vaccination schedule for your dog based on their age, lifestyle, and local regulations. Remember, prevention is key in safeguarding your furry friend from these preventable diseases.
Non-Core Vaccinations for Dogs
Bordetella Vaccine
The Bordetella vaccine is a non-core vaccination strongly recommended for dogs, particularly those regularly exposed to other dogs in settings such as boarding facilities, dog parks, or training classes. Bordetella bronchiseptica is a bacterium that causes kennel cough, a highly contagious respiratory disease in dogs. The vaccine helps to protect dogs from this unpleasant and potentially dangerous illness.
Kennel cough is easily transmitted through airborne droplets or direct contact with infected dogs. Symptoms include a persistent cough, sneezing, runny nose, and fever. It can lead to more severe respiratory complications if left untreated. By vaccinating your dog against Bordetella, you can minimize the risk of them contracting kennel cough and spreading it to other dogs.
Lyme Disease Vaccine
The Lyme disease vaccine is another non-core vaccination that is recommended for dogs living in or visiting areas where ticks carrying the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi are prevalent. Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness that can cause serious health issues in dogs as well as humans.
Ticks are commonly found in wooded areas, tall grasses, and even in urban parks. When an infected tick bites a dog, it can transmit the bacteria, leading to Lyme disease. Symptoms of Lyme disease in dogs include lameness, swollen joints, fever, loss of appetite, and lethargy. In severe cases, it can even affect the kidneys and nervous system.
Vaccinating your dog against Lyme disease reduces the risk of infection and complications. It’s crucial to understand that the vaccine doesn’t guarantee 100% protection. Implementing additional measures, such as regular tick checks and using tick repellents, remains essential for comprehensive tick prevention.
Leptospirosis Vaccine
Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection that can affect both dogs and humans. It is transmitted through contact with the urine of infected animals, such as rodents, wildlife, or other dogs. Dogs can contract the bacteria by drinking contaminated water or coming into contact with contaminated soil.
Leptospirosis can cause severe damage to the kidneys, liver, and other organs. Symptoms include fever, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, and jaundice. In some cases, it can be fatal if left untreated.
The leptospirosis vaccine is advisable for dogs residing in or regularly visiting regions with a high prevalence of the disease. Additionally, dogs engaged in activities or possessing lifestyles that elevate their risk of exposure should be prioritized for vaccination. By vaccinating your dog against leptospirosis, you can help protect them from this potentially life-threatening infection.
Ensuring that your dog receives the essential vaccinations is crucial for protecting their health and well-being. Vaccinations not only prevent the spread of harmful diseases but also safeguard your dog from potential life-threatening illnesses. By staying up-to-date with your dog’s vaccinations, you can provide them with a strong immune system and a longer, healthier life. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate vaccination schedule for your dog based on their age, lifestyle, and potential exposure risks. With proper vaccination, you can give your furry companion the best chance for a happy and disease-free life.